 Image credit: Yuan Liao
Image credit: Yuan LiaoAbstract
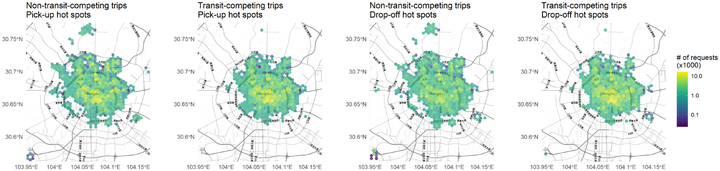
Ride-sourcing risks increasing GHG emissions by replacing public transit (PT) for some trips therefore, understanding the relation of ride-sourcing to PT in urban mobility is crucial. This study explores the competition between ride-sourcing and PT through the lens of big data analysis. This research uses 4.3 million ride-sourcing trip records collected from Chengdu, China over a month, dividing these into two categories, transit-competing (48.2%) and non-transit-competing (51.8%). Here, a ride-sourcing trip is labelled transit-competing if and only if it occurs during the day and there is a PT alternative such that the walking distance associated with it is less than 800m for access and egress alike. We construct a glass-box model to characterise the two ride-sourcing trip categories based on trip attributes and the built environment from the enriched trip data. This study provides a good overview of not only the main factors affecting the relationship between ride-sourcing and PT, but also the interactions between those factors. The built environment, as characterised by points of interest (POIs) and transit-stop density, is the most important aspect followed by travel time, number of transfers, weather, and a series of interactions between them. Competition is more likely to arise if: (1) the travel time by ride-sourcing <15min or the travel time by PT is disproportionately longer than ride-sourcing; (2) the PT alternative requires multiple transfers, especially for the trips happening within the transition area between the central city and the outskirts; (3) the weather is good; (4) land use is high-density and high-diversity; (5) transit access is good, especially for the areas featuring a large number of business and much real estate. Based on the main findings, we discuss a few recommendations for transport planning and policymaking.